Oral Presentation HUPO 2019 - 18th Human Proteome Organization World Congress
Carcinoembryonic antigen targeted glycomics and glycoproteomics reveals novel features of human glycosylation (64694)
Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) is an FDA-approved tumour marker strongly associated with tumour progression and metastasis. With 28 potential sites of N-glycosylation, CEA is densely coated with glycans, however, the diagnostic potential embedded in its glycosylation to improve the selectivity of current cancer diagnostics is under-utilised.
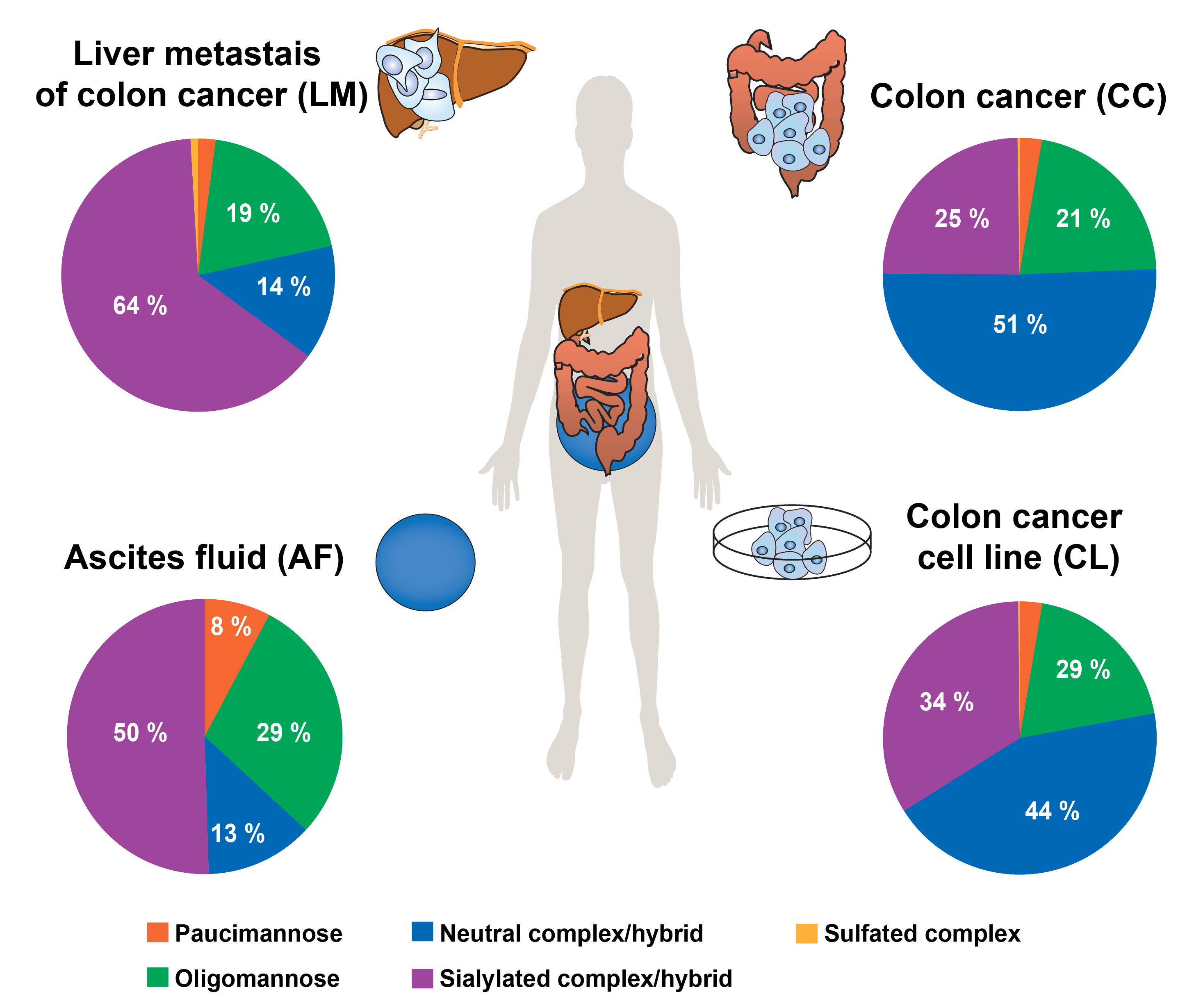
The glycosylation of CEA purified from four different body sources [human colon cancer (cell line and tissue), tissue from liver metastasis of colon cancer and ascites fluid] was investigated by porous-graphitised-carbon (PGC) LC-ESI-MS/MS glycomics, while CEA glycosylation sites where mapped using glycopeptides obtained by pronase digestion and analysed on a dual LC system combining reverse-phase and PGC chromatography within a single LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis.
The analysed CEAs exhibited 278 individual N-glycan structures, which vastly increases our knowledge on CEA N-glycosylation and makes it the most heterogeneously N-glycosylated protein known to date. Despite this huge diversity, CEA N-glycosylation carries body origin-specific glycosylation signatures, including an unusual glyco-epitope containing a b1-4 galactosidase resistant hexose attached to the bisecting GlcNAc. This hitherto unknown glyco-epitope was in particular present on colon derived CEA, while almost absent in any other CEAs analysed. Other distinct glycosylation differences such as N-glycan branching, degree of sialylation and level of bisecting N-glycans were uncovered between the CEA's from different body sources. Antennae fucosylation, such Lex and Leb/y determinants were present in all CEAs, however with significant abundance differences between the different sources. Next to confirming that 27 out of the 28 predicted N-glycosylation sites are glycosylated, we also identified a novel, 29th site of N-glycosylation on Asn76 that is located within a non-canonical 71N-R-Q73 sequence motif in the N-domain.
In summary, CEA-specific glycosylation bears a yet unmined potential to improve the specificity of the CEA-marker, but also to understand the role glycosylation plays for its function.